The coronavirus storm has hit many parts of the world and generated tremendous impacts on people’s lives. In crises like this, people seek information to assess the situation and to protect themselves and their loved ones. However, there are concerns about the credibility and neutrality of information circulated in the virtual space. The Center for Media & Communication Research at the Hong Kong Baptist University invited three speakers to share their observation with participants in a virtual format on April 3, 2020. Here I share excerpts and resources from the discussion useful for journalists, health professionals, fact checkers, educators, organisations engaged in civil/information literacy and interested public at large.
Moderator:
Leanne Chang, Director of the Centre for Media and Communication Research, Hong Kong Baptist University
Speakers:
Summer Chen, Chief Editor of Taiwan FactCheck Center
Masato Kajimoto, Director of Annie Lab; Assistant Professor of Practice, Journalism and Media Studies Centre, University of Hong Kong
Rose Luqiu, Assistant Professor, Department of Journalism, Hong Kong Baptist University
Summer’s talk:
We are certified with the International Fact-Checking Network (IFCN) for the second year now.
After covering the Taiwan Presidential Elections we are fighting against Coronavirus misinformation.
Last December we became an independent foundation. We cooperate with popular social media in Taiwan which includes, Facebook, Google Claim Review, Line, Yahoo.
We have a large database of fact checks on COVID 19. We have already debunked 110 myths.
Battleline in Taiwan:
1- interview experts, scientists & doctors, 2- support from Science Media Center Taiwan (Academic support is important to build our own knowledge gap on the virus), 3- fact-checking Central Epidemic Command Center (since we are independent from government we do not just report Taiwan government suggestions).
Battleline around the globe:
1- The IFCN comprises of 65 fact-checking organisations from 45 countries. They have collected more than 1500 fact checks under the umbrella of CoronaVirusAlliance. See their Poynter database below:
Misinformation timeline in Taiwan (what we have debunked so far):
Jan (first case in Taiwan) – Remedies, Cures, Measures, Virus character.
Feb: Mostly news stories, conspiracies mixed with science papers.
March: Taiwan government is losing control (debunked almost 10 ‘facts’ about this topic). We did digital literacy campaign for the public to help identify this kind of information.
March – now: Virus is from US, or Italy not Wuhan (probably China propaganda).
March middle: Italy thanks China (also propaganda by China).
March middle-end: Lockdown policies. US is losing control (misinformation regarding this subject, 9 fact checks).
Current misinformation: #Malicious message “go stock pile supplies”, #Remedies #Cures.
Interesting academic ideas/topics she recommends for research/stories:
- There are now two database, IFCN, TFC. Any database can be used for research how one piece of misinformation spreads around the world. For instance, Garlic Soup can cure COVID-19 or Windy data proves there are 40,000 corpses burning in Wuhan. You can see that many other countries reported similar false information. https://www.poynter.org/ifcn-covid-19-misinformation/?search_terms=corpses. https://tfc-taiwan.org.tw/articles/2366.
- Study on health misinformation about COVID-19. Specially, reports claiming to quote celebrities, relatives, other influencers.
- China’s propaganda; corona virus is not from Wuhan but US or Italy. Italians appreciate China; research on how these misinformation networks are built, how they spread etc.
- If we compare misinformation about Hong Kong protest and COVID-19 we can find similar patterns of misinformation, conducted by China. One pattern: Spokesman + state-backed media + other materials spread on social media.
- Comparison of misinformation on COVID 19, specially on social media, to examine how some is debunked while other is not.
- Researching on misinformation about COVID 19 being spread also from other political actors such as Falun Gong (a movement banned in China).
Masato’s talk:
I have some observations based on my experience but not based on specific research:
- Knowledge gap amoung us (ordinary citizens, the news media, media experts). We all have some knowledge but the gap means misinformation spreads rapidly.
- Relatedly, “legit” traditional media not just “bad media organisations” that are amplifying fears and misleading claims. Something not discussed enough.
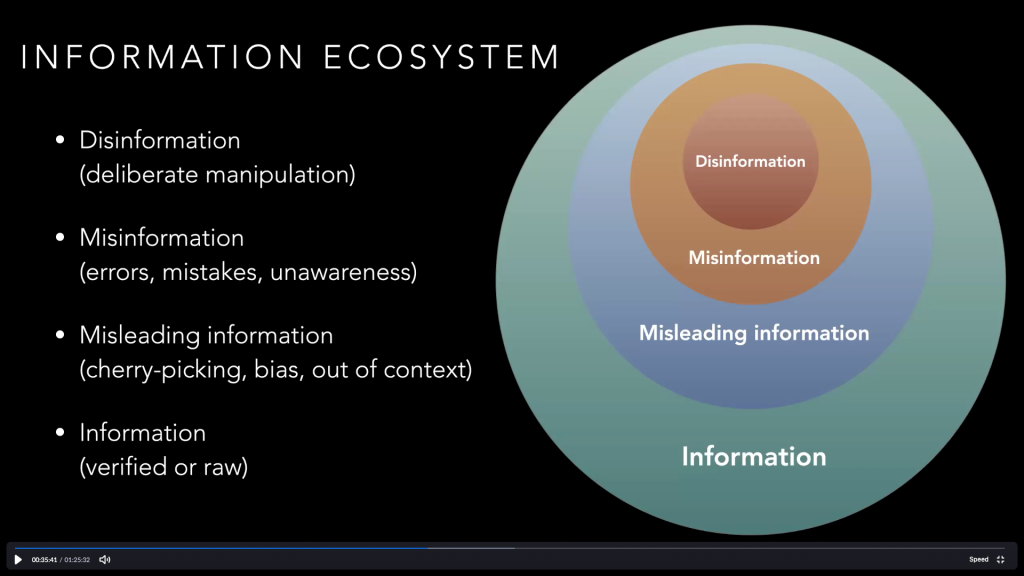
- Misinformation is a problem, fact-checking helps but this is as much a public health communication problem where we must address the larger information ecosystem on COVID 19.
Knowledge gap
– Experts and journalist often ignore misinformation. They do not see news value in digging through it, since they are able to see through it quickly dismiss it. In other words, experts that are normally critical thinkers, may not see how the ordinary audience is reacting and sharing misinformation.
For instance; warm water can kill coronavirus. Has become a huge international phenomenon. A popular remedy being reported on social media in Canada, Philippines, India, Cambodia, Japan, Brazil, Indonesia, Spain, Venezuela.
A small claim that has universal appeal with potentially dangerous consequences for management of COVID 19.
Journalist think this misinformation is harmless. But if you are in fact-checking field, you realize how many people actually believe in it do not take other precautions. They don’t wash hands. They go out freely. Then they are telling their friends on social media how things are all ok.
– I run the database Annie Lab. http://annielab.org.
We are in talks with Google as well to take into account our database. Hopefully you would not have to visit our database and can identify information organically.
Role of journalists

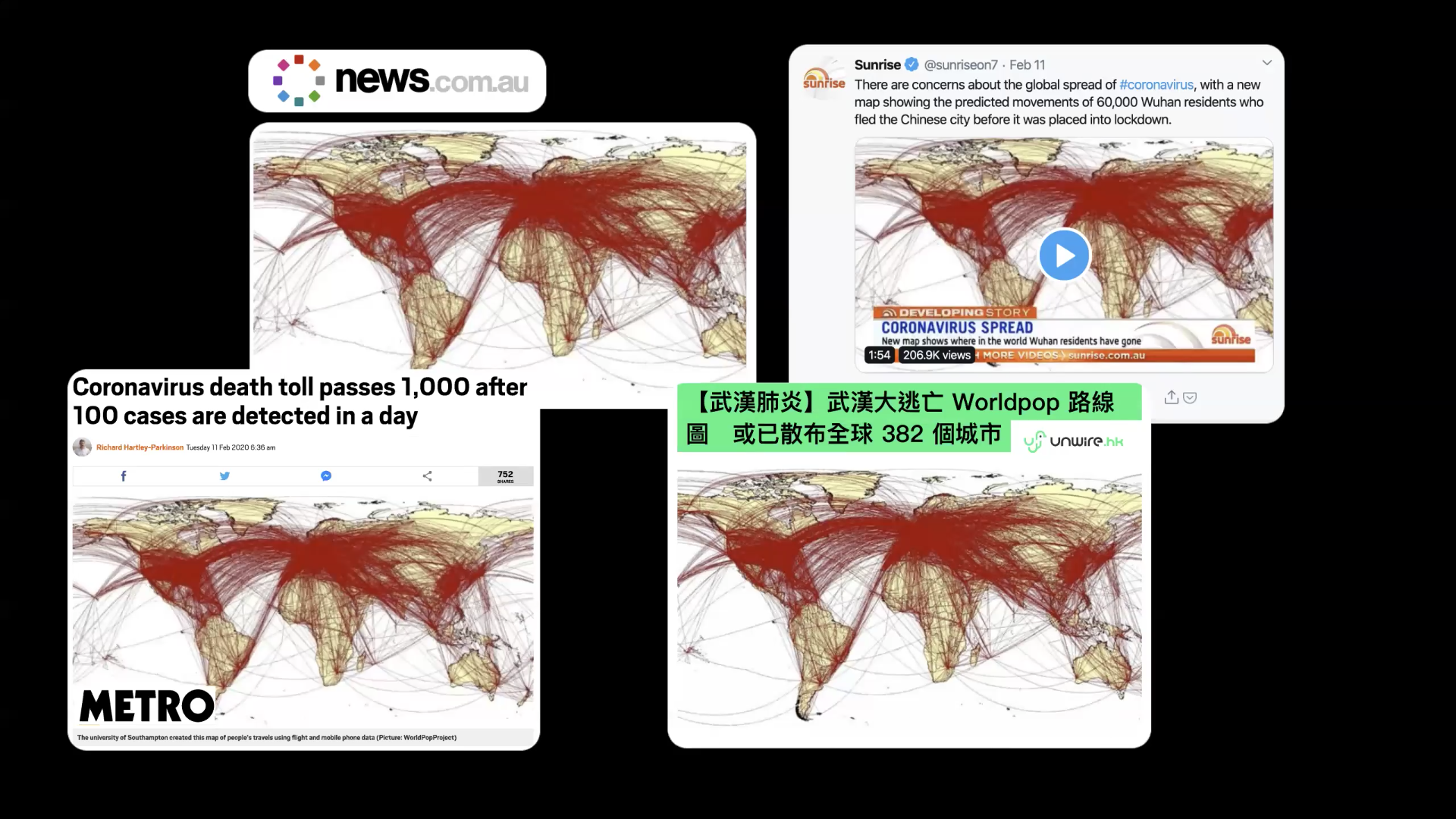
This map was going strong in many parts of the world. It came from a university in the UK. I forgot the name. It was used along with a research paper to illustrate how people travel around the world by airplane.
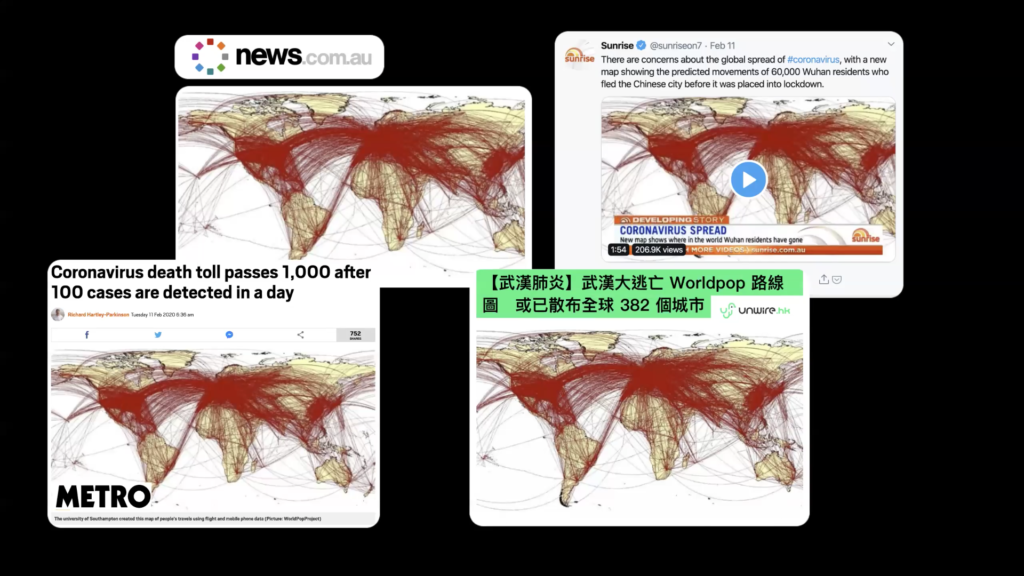
But many people interpreted it as how people have travelled the world from Wuhan before the city got shut down in January. News organizations in many countries carried the story.
– There are five types of COVID-19 misinformation in my view. I think many fact-checkers would agree:
- Origin
- Symptoms
- Miracle treatment/cure
- Reactions (panic, abandoned bodies, violence, etc.)
- Government responses (stats manipulation, lockdown, etc.)
– Fact-checking ‘future’ is not possible; example, a story on how China will close down its factories that make toilet paper.
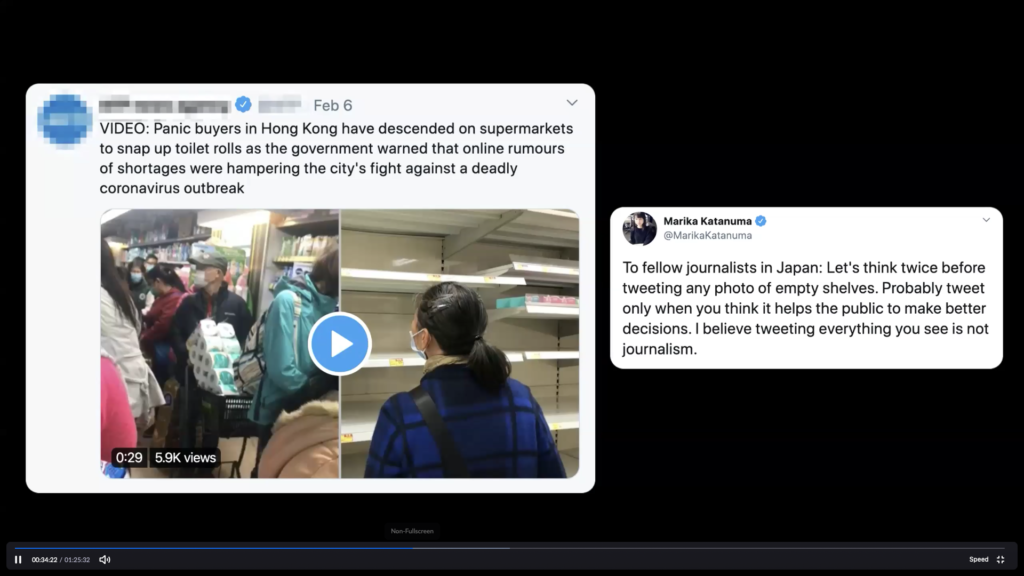
– If you are a journalist reporting a story, not fact-checking, but reporting, an instance of people panic buying toilet paper is now a story.
We detected early on Annie Lab that this rumour on toilet paper is going viral in Hong Kong. I work from home now with my students since university is closed so when my students initially pointed this out, I ignored them thinking who will believe such a rumour. But people were posting videos of empty shelf, people queing, etc. These were reshared online and covered by traditional media.
As one result, news organisations report on toilet paper shortage actually pushed people into panic buying since they believed in the shortage. The huge spike in demand obviously effected the supply side in Hong Kong. The story that was rather groundless became true. News organisations are partly to blame.
COVID 19 episode tells us that news presentation style is important. It operates at a psychological level.
Misinformation
What to do about it?
Time to think about responsible pandemic news coverage. We have an industry guideline for suicide reporting in many countries already. Why not a similar guidline for health communication/pandemic reporting? Currently, this is a wild west.
Finally, reporting, fact-checking on epidemic is not easy when even experts sometimes disagree on subjects. For example, should we encourage or discourage aircon use? Fact checking can be misleading too.
I recommend these must read articles for journalists:

Useful comments during Q&A:
Masato says that’s there is no way to fight misinformation through fact-checking. Purpose of fact-checking is not to correct everyone who has read misinformation. People move on from one rumor to another. Many rumors are created all the time.
Fact checking does help to straighten the historical record.
But it is better understood as a digital literacy program. By fact-checking we are showing the public how to handle information. If news consumers are doing fact-checks on the demand side, then this problem can be improved.
While it’s news media’s responsibility it’s the public’s responsibility also.
Summer says that many of the claims that are received at the Taiwan Fact-Check Center are by the general public. So it’s important to bring the public into confidence. When we fact check, we are not focused on conclusion. Our articles are detailed with interviews, counterclaims etc. We want to show the public the process of reading our articles and the content itself. This will also help ordinary people to learn fact-checking.
We want people to see fact checking as a social program. A social movement.
How can we separate fact from opinion?
Masato says I give my students statements to verify. For instance, Japanese Food is better than Chinese Food – is it an opinion or fact? If this is a fact than based on what data? Is it the medical literature, scientific literature, what is the definition of Japanese Food? Is fried rice Chinese or Japanese. I give my students such exercises.
Summer says fact checking can also backfire when people upon learning about a false information may still choose to believe it. They may think for instance a fact checked story is against values of Taiwan.
Summer also says that news reports on the pandemic may also make more sense in one context compared to another. Such as the limited use of face mask in Texas, United States. Perhaps open spaces mean people are not wearing masks. But in Taiwan such advise would be nonsense. These reports have more to do with field of journalism rather than fact-checking.
Other resources:
Recommended article on mask debate: https://www.theatlantic.com/health/archive/2020/04/coronavirus-pandemic-airborne-go-outside-masks/609235/
Resource on information literacy by Prof. Masato: https://medium.com/@MasatoKJ
This six-week course developed by the University of Hong Kong and State University of New York will help learners develop their critical thinking skills to enable them to better identify reliable information in news reports: https://www.coursera.org/learn/news-literacy
Links to the cloud files on the original discussion: